
PEG-Boronic Acid for Glycan PEGylation
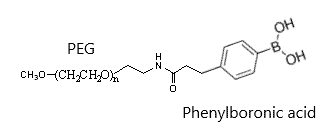
Properties
We provide custom synthesis of a variety of PEG-Boronic acid reagents including:
mPEG-Boronic acid MW 350, 550, 750, 1k, 2k, 5k, 10k, 20k, 30k and 40k
Boronic acid-PEG-Boronic acid MW 600, 1k, 2k, 3.4k, 5k, 10k, 20k and 30k
4-arm PEG-Boronic acid MW 2k, 5k, 10k and 20k
8-arm PEG-Boronic acid MW 10k, 20k and 40k
Maleimide-PEG-Boronic acid MW 1k, 2k, 3.4k, 5k and 10k
Acrylate-PEG-Boronic acid MW 1k, 2k, 3.4k, 5k and 10k
Biotin-PEG-Boronic acid MW 1k, 2k, 3.4k, 5k and 10k
FITC-PEG-Boronic acid MW 1k, 2k, 3.4k, 5k and 10k
and many others
Get In Touch
If you have any questions, please submit an online inquiry.
"*" indicates required fields
