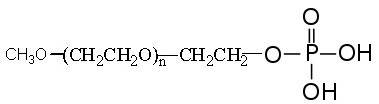Description
mPEG Phosphate is useful to PEGylate metal oxide particles and surfaces to form stable monolayer protection. The strong binding properties of organophosphorus to metal oxides result from the creation of a stable M-O-P structure via phosphate metal coordinative interactions. PEG Phosphate-based coupling agents form self-assembled monolayer on the surface of metal oxide nanoparticles such as iron oxide, superparamagnetic particles and upconverting and down-conversion nanoparticles to form thermodynamically stable nanoparticle dispersion. Bifunctional PEG phosphate reagents are available via custom synthesis. Phosphate is the salt form of phosphoric acid.
Properties
Molecular weight: MW of PEG was measured by MALDI-MS or GPC. PDI (polydispersity index) of our linear PEG is 1.02-1.05 with very narrow MW distribution. The number of repeating ethylene oxide units (CH2CH2O) or the degree of polymerization is calculated dividing the PEG MW by 44 (44 is the molecular mass of one repeating unit).
Solubility: Soluble in water and aqueous buffer, chloroform, methylene chloride, DMF, DMSO, and less soluble in alcohol. Not soluble in ether. mPEG phosphate may have reduced solubility in less polar organic solvent if present as negatively charged phosphate salt.
Density: PEG density is approximately 1.125 g/mL
Physical form: PEG products generally appear as white or off-white powder.
Storage condition: PEG product shall be stored in the original form as received in a freezer at -20C or lower for long term storage. Stock solution of PEG reagents that do not contain oxygen or moisture sensitive functional groups may be temporarily stored in a refrigerator or ambient temperature for multiple days. Stock solution should avoid repeated freeze-and-thaw cycles. See Documents section for detailed storage and handling conditions.