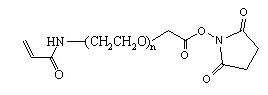
Description
Acrylamide-PEG-SCM is a linear heterobifunctional PEG reagent with an Acrylamide (ACA) and an activated NHS ester. The C=C double bond is connected to PEG via an amide bond. It is a useful crosslinking reagent with a PEG spacer. Acrylamide can polymerize with UV light or radical initiator. SCM is one type of NHS esters, often called succinimidyl carboxyl methyl (SCM) ester. SCM is very reactive with primary amine to form a stable amide bond. Acrylamide-PEG-SCM may be used to introduce an amine reactive functional group in crosslinked PEG hydrogel.
Properties
Molecular weight: MW of PEG was measured by MALDI-MS or GPC. PDI (polydispersity index) of our linear PEG is 1.02-1.05 with very narrow MW distribution. The number of repeating ethylene oxide units (CH2CH2O) or the degree of polymerization is calculated dividing the PEG MW by 44 (44 is the molecular mass of one repeating unit).
Solubility: Soluble in water and aqueous buffer, chloroform, methylene chloride, DMF, DMSO, and less soluble in alcohol, toluene. Not soluble in ether.
Density: PEG density is approximately 1.125 g/mL
Physical form: PEG products generally appear as white or off-white powder, and for very low MW linear PEG such as MW 1k or less, it may appear as wax-like, semi-solid material due to the low MW and the type of functional groups.
Storage condition: PEG product shall be stored in the original form as received in a freezer at -20C or lower for long term storage. Stock solution of PEG reagents that do not contain oxygen or moisture sensitive functional groups may be temporarily stored in a refrigerator or ambient temperature for multiple days. Stock solution should avoid repeated freeze-and-thaw cycles. See Documents section for detailed storage and handling conditions.
References
1. Protein Conjugation (Amine PEGylation) to PEG Hydrogel – Bioartificial matrices for therapeutic vascularization, Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010; 107(8): 3323–3328, Text.
2. Crosslinking Proteins to PEG Hydrogels – Injectable laminin-functionalized hydrogel for nucleus pulposus regeneration, Biomaterials, 2013 (34): 7381-7388, Text.
3. Crosslinking Proteins to PEG Hydrogels – Photocrosslinkable laminin-functionalized polyethylene glycol hydrogel for intervertebral disc regeneration, Acta Biomaterialia 10 (2014) 1102–1111, Text.
4. Bioartificial matrices for therapeutic vascularization. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 107.8 (2010): 3323-3328. Text.
5. PEG-PCL Hydrogel and Conjugation of Proteins – Shape Memory RGD-Containing Networks: Synthesis, Characterization, and Application in Cell Culture, Macromol. Symp. 2011, 309/310, 162–172,Text.
6. Preparation of Protein–Polymer Conjugates: Copolymerisation by RAFT, 2020, DOI: 10.1071/CH19514
Click here to view an expanded list of hundreds of publications citing Creative PEGWorks products.