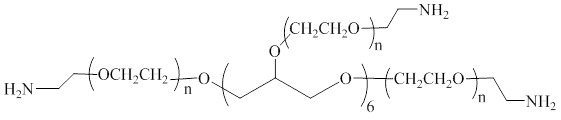
Description
8-Arm PEG-Amine is a multiarm PEG derivative with amine groups at each terminal of the eight arms connected to one hexaglycerol core. The reactive primary amine or NH2 group can rapidly react with activated carboxyl acid such as NHS ester to form stable amide bonds.
Properties
Molecular weight: 8-Arm PEG MW refers to the MW of the entire PEG molecule. The MW of each arm is 1/8 of the MW indicated in the product name. MW of PEG was measured by MALDI-MS or GPC. PDI (polydispersity index) of our 8-Arm PEG is 1.02-1.06 with very narrow MW distribution. The number of repeating ethylene oxide units (CH2CH2O) or the degree of polymerization is calculated dividing the PEG MW by 44 (44 is the molecular mass of one repeating unit).
Solubility: Soluble in water and aqueous buffer, chloroform, methylene chloride, DMF, DMSO, and less soluble in alcohol, toluene. Not soluble in ether.
Density: PEG density is approximately 1.125 g/mL
Physical form: PEG products generally appear as white or off-white powder, and for certain special 8-arm PEGs, it may appear as wax-like, semi-solid material due to low MW and the type of functional groups.
Storage condition: PEG product shall be stored in the original form as received in a freezer at -20C or lower for long term storage. Stock solution of PEG reagents that do not contain oxygen or moisture sensitive functional groups may be temporarily stored in a refrigerator or ambient temperature for multiple days. Stock solution should avoid repeated freeze-and-thaw cycles. See Documents section for detailed storage and handling conditions.
References
1. Crosslinked PEG Microspheres and Hydrogels – Long term culture of HL-1 cardiomyocytes in modular poly(ethylene glycol) microsphere-based scaffolds crosslinked in the phase separated state. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8(1): 31-40, Text.
2. Rapid detection of polyethylene glycol sonolysis upon functionalization of carbon nanomaterials. Experimental Biology and Medicine (2015): 1535370214567615. Text
3. Electrospun catechol-modified poly (ethyleneglycol) nanofibrous mesh for anti-fouling properties. Journal of Materials Chemistry B 1.32 (2013): 3940-3949. Text
4. Engineering Poly (ethylene glycol) Particles for Improved Biodistribution.” ACS nano 9.2 (2015): 1571-1580. Text
5. Shape-Preserved Transformation of Biological Cells into Synthetic Hydrogel Microparticles, Advanced Biosystems, 2019, Text.
6. 3D Bioprinting using UNIversal Orthogonal Network (UNION) Bioinks, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 2007983, Text.
Click here to view an expanded list of hundreds of publications citing Creative PEGWorks products.