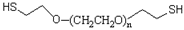Properties
Molecular weight: MW of PEG was measured by MALDI-MS or GPC. PDI (polydispersity index) of our linear PEG is 1.02-1.05 with very narrow MW distribution. The number of repeating ethylene oxide units (CH2CH2O) or the degree of polymerization is calculated dividing the PEG MW by 44 (44 is the molecular mass of one repeating unit).
Solubility: Soluble in water and aqueous buffer, chloroform, methylene chloride, DMF, DMSO, and less soluble in alcohol, toluene. Not soluble in ether.
Density: PEG density is approximately 1.125 g/mL
Physical form: PEG products generally appear as white or off-white powder, and for very low MW linear PEG such as MW 1k or less, it may appear as wax-like, semi-solid material due to the low MW and the type of functional groups.
Storage condition: PEG product shall be stored in the original form as received in a freezer at -20C or lower for long term storage. Stock solution of PEG reagents that do not contain oxygen or moisture sensitive functional groups may be temporarily stored in a refrigerator or ambient temperature for multiple days. Stock solution should avoid repeated freeze-and-thaw cycles. See Documents section for detailed storage and handling conditions.
References
1. Injectable laminin-functionalized hydrogel for nucleus pulposus regeneration, Biomaterials, 2013 (34): 7381-7388, Text.
2. Ultralow protein adsorbing coatings from clickable PEG nanogel solutions: Benefits of attachment under salt-induced phase separation conditions and comparison with PEG/albumin nanogel coatings. Langmuir 29.12 (2013): 4128-4139. Text.
3. Clickable Poly (ethylene glycol)-Microsphere Based Cell Scaffolds. Macromolecular chemistry and physics 214.8 (2013): 948-956. Text.
4. Design of interpenetrating chitosan and poly(ethylene glycol) sponges for potential drug delivery applications Carbohydrate Polymers, 2017, Pages 166-175, Text.
5. Time-Controllable Lipophilic-Drug Release System Designed by Loading Lipid Nanoparticles into Polysaccharide Hydrogels, Macromolecular Biosciences, Issue 9, 2017, 1700045, Text.
6. Effect of end-grafted polymers conformation on protein resistance. Langmuir. 2018 Jan 12. Text.
7. Synthetic hydrogels formed by thiol ene crosslinking of vinyl sulfone-functional poly (methyl vinyl ether-alt-maleic acid) with dithio-polyethyleneglycol. Soft Matter. 2018. Text.
8. Opposing temperature dependence of the stretching response of single PEG and PNiPAM polymers, J. Am. Chem. Soc.2019, Text.
9. Engineered 3D hydrogels with fibronectin that sequester and present growth factors, Biomaterials, 2020, Text.
10. A Rapid Crosslinkable Maleimide-Modified Hyaluronic Acid and Gelatin Hydrogel Delivery System for Regenerative Applications, Gels, 2021, 7(1), 13, Text.
11. A Hydrogel Platform that Incorporates Laminin Isoforms for Efficient Presentation of Growth Factors – Neural Growth and Osteogenesis, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2010225, Text.
12. Development of a library of laminin-mimetic peptide hydrogels for control of nucleus pulposus cell behaviors, J Tissue Eng. 2021 Jan-Dec; 12: 20417314211021220. Text.
13. Bioactive in situ crosslinkable polymer-peptide hydrogel for cell delivery to the intervertebral disc in a rat model, Acta Biomaterialia, 2021, 117-127, Text.
14. Gated Photoreactivity of Pyrene Copolymers in Multiresponsive Cross-Linked starPEG-Hydrogels, ACS Polym. Au 2021, 1, 1
Click here to view an expanded list of thousands of publications citing Creative PEGWorks products.