Description
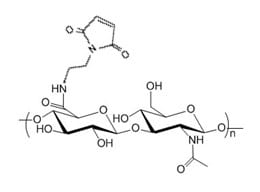
Hyaluronate Mono Maleimide is a HA derivative with one reactive maleimide group. Maleimide (MAL) selectively reacts with free thiol via Michael addition to form a stable carbon sulfur bond (thiosuccinimide). HA-MAL can be used for site specific protein and peptide modification at the cysteine amino acid site. The thiol group to react with HA-Maleimide needs to be in the form of free thiol, and often a reducing reagent agent DTT and preferably TCEP (without the need to remove excessive TCEP) is used to enhance the thiol reactivity.
The maleimide group is attached to HA through an amide bond at the reducing end of HA polymer chain. Purity: >95% powder. Degree of substitution: mono - one maleimide group per HA polymer.
Properties
Name and Source: Hyaluronic acid (HA, Hyaluronan, Hyaluronate) is an anionic, non-sulfated glycosaminoglycan distributed widely throughout connective, epithelial, and neural tissues. CAS# 9004-61-9. Our HA products are produced via microbial fermentation. See Documents section for details.
Appearance: White, lyophilized powder.
Solubility: Soluble in water and the solubility data varies with MW. Higher MW results in lowered solubility. Typically solubility ranges 5-50 mg/mL, that is, 0.5%-5%. Buffered solution at pH >6 enhances solubility due to deprotonation of carboxylic acid groups and formation of carboxylate salts. HA derivatives with hydrophobic groups will lower the solubility in water, and adding alcohol or DMSO to an alcohol-water or DMSO-water mixture can dramatically improve the solubility up to 200 mg/mL (20%).
Degree of Substitution (DoS): There is one maleimide group per HA polymer chain.
References
1. Chemical modification of hyaluronic acid by carbodiimides, Bioconjugate chemistry, 1991, 2(4):232-41.
2. Hyaluronic acid based scaffolds for tissue engineering—A review, Carbohydrate Polymers 2013, 92(2):1262– 1279
Click here to view an expanded list of hundreds of publications citing Creative PEGWorks products.