Description
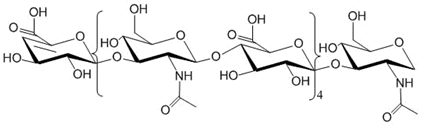
Discrete-HA Oligomer HA8 as shown in the molecular structure has 8 monosaccharide units (4 repeating disaccharide units) and one reducing end and one non-reducing end units. For all of our oligomer HAn products, n refers to the number of the monosaccharide units excluding both reducing and non-reducing terminal units.
Discrete-HA oligomer is oligomeric hyaluronic acid produced by enzymatic degradation of high molecular weight HA followed by chromatographic separation. C4-C5 unsaturated hexuronic acid at the non-reducing end of the oligosaccharides produced by endolyase scission of the HA polymer. Discrete-HA oligomers have 95% or greater purity.
Properties
Name and Source: Hyaluronic acid (HA, Hyaluronan, Hyaluronate) is an anionic, non-sulfated glycosaminoglycan distributed widely throughout connective, epithelial, and neural tissues. CAS# 9004-61-9. Our HA products are produced via microbial fermentation. See Documents section for details.
Appearance: White, lyophilized powder.
Solubility: Soluble in water and the solubility data varies with MW. Higher MW results in lowered solubility. Typically solubility ranges 5-50 mg/mL, that is, 0.5%-5%. Buffered solution at pH >6 enhances solubility due to deprotonation of carboxylic acid groups and formation of carboxylate salts. HA derivatives with hydrophobic groups will lower the solubility in water, and adding alcohol or DMSO to an alcohol-water or DMSO-water mixture can dramatically improve the solubility up to 200 mg/mL (20%).
References
Interactions of cartilage proteoglycans with hyaluronate. Inhibition of the interaction by modified oligomers of hyaluronate. 1979, J. Biol. Chem. 254(11):4624-4630