
PEGylated Hyaluronic Acid
Properties
Name and Source: Hyaluronic acid (HA, Hyaluronan, Hyaluronate) is an anionic, non-sulfated glycosaminoglycan distributed widely throughout connective, epithelial, and neural tissues. CAS# 9004-61-9. Our HA products are produced via microbial fermentation. See Documents section for details.
Appearance: White, lyophilized powder, except dye-labeled HA reagents.
Solubility: Soluble in water and the solubility data varies with MW. Higher MW results in lowered solubility. Typically solubility ranges 5-50 mg/mL, that is, 0.5%-5%. Buffered solution at pH >6 enhances solubility due to deprotonation of carboxylic acid groups and formation of carboxylate salts. PEGylated HA is highly water soluble, and reasonably soluble in DMSO, and insoluble in most of other organic solvents.
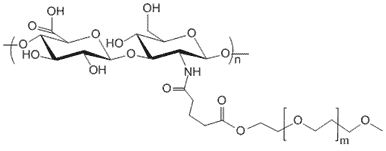
Degree of Substitution (DoS): The standard DoS is 5% by default. Product variants with special DoS other than 5% is indicated in the product name and catalog number. For example, HA-301-30% means that the DoS is 30% for this particular product.
The substitution or labeling ratio is the percentage of HA disaccharide monomers that are functionalized with the functional groups. You may calculate the number of functional groups in each HA polymer chain by 1) dividing the MW of HA by the MW of one disaccharide monomer to derive the number of disaccharide monomers in HA; 2) then multiple the number of disaccharide monomers by the labeling ratio or DoS to get the number of functional groups in each HA polymer. See Documents section for details.
Get In Touch
If you have any questions, please submit an online inquiry.
"*" indicates required fields
