Description
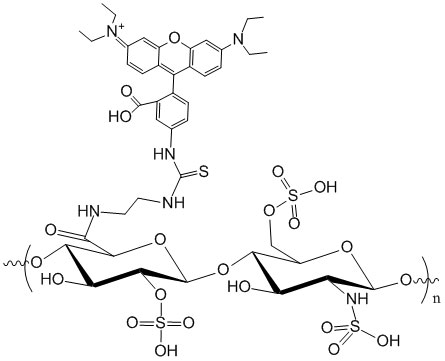
Heparin Rhodamine is a fluorescent heparin polysaccharide. Heparin is functionalized with rhodamine, Ex/Em wavelength 552/575 nm. Purity: >95% powder. Degree of substitution: 1 mol % substitution and at least one dye molecule per HP polymer. HP labeled with other types of rhodamine dyes such as Texas Red, Sulforhodamine 101 may be available through our custom synthesis.
Properties
Heparin is a member of the glycosaminoglycan family of carbohydrates (which includes the closely related molecule heparan sulfate) and consists of a variably sulfated repeating disaccharide unit. The most common disaccharide unit in heparin is composed of a 2-O-sulfated iduronic acid and 6-O-sulfated, N-sulfated glucosamine, IdoA(2S)-GlcNS(6S).
Heparin CAS#: 9005-49-6
References
1. Heparin Mimics Extracellular DNA in Binding to Cell Surface-Localized Proteins and Promoting Staphylococcus aureus Biofilm Formation, mSphere 2:e00135-17, 2017, Text.
2. Heparin-Engineered Mesoporous Iron Metal-Organic Framework Nanoparticles: Toward Stealth Drug Nanocarriers, Advanced Healthcare Materialsï ¼Å’2015, 4(8), pp 1246-1257.
3. Modified Fluorescent Technique, Using Rhodamine, for Studies of Rhizobium japonicum-Soybean Symbiosis, Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 June; 37(6): 1243-1244.
4. Binding of heparin to antithrombin III: The use of dansyl and rhodamine labels, Archives of biochemistry and biophysics, 1980, 205(2), 315-22.
5. ApoE: In Vitro Studies of a Small Molecule Effector, Biochemistry, 2016, 55 (18), pp 2613-2621, Text.
6. Transmembrane Protein 184A Is a Receptor Required for Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Responses to Heparin. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2016 Mar 4;291(10):5326-41. Text.
7. Regulatory mechanisms of tau protein fibrillation under the conditions of liquid-liquid phase separation, PNAS, 2021, Text.
Click here to view an expanded list of hundreds of publications citing Creative PEGWorks products.